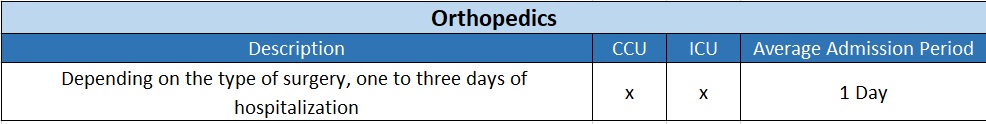
What is orthopedics?
Orthopedics is a medical specialty dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention of injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system of the human body, which includes the bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves that allow a person to move and be active. This field of medicine is concerned with the treatment of congenital abnormalities, the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases, and injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
Currently, orthopedics is dedicated to patients of all ages, from infants with a crooked or twisted foot to young athletes who need arthroscopic surgery. The field also deals with the treatment of bone fractures.
When should we see an orthopedic doctor?
1. Chronic pain
2. Injuries and fractures
3. Decreased mobility and flexibility
4. Swelling and inflammation
5. Increasing disability
6. Joint and muscle problems in the elderly
What diseases does an orthopedic doctor treat?
1. Sprains and strains of joints
2. Muscle strains
3. Fractures and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae
4. Fractures of the thoracic spine
5. Fractures and dislocations of the lumbar spine
6. Fractures of the sacrum and coccyx
7. Fractures and dislocations of the clavicle
8. Fractures of the humerus
9. Fractures and dislocations of the elbow joint and forearm bones
10. Fractures and dislocations of the wrist, palm and finger bones
11. Fractures and dislocations of the pelvis
12. Fractures of the ribs
13. Injuries to the costal cartilages
14. Fractures of the sternum
15. Fractures and dislocations of the hip joint
16. Fractures and dislocations of the patella
17. Fractures of the shin bones
18. Ankle and toe injuries
19. Back pain
20. Intervertebral disc injuries and diseases
Spinal deformity
21. Rheumatic diseases of joints and bones
22. Bone tuberculosis
23. Congenital abnormalities and diseases of bones and joints Shoulder joint and muscle injuries
24. Bone and muscle tumors
25. Tendon injuries and cuts
26. Joint osteoarthritis
27. Femoral head necrosis (blackening)
28. Knee ligament and tendon injuries and disorders
29. Hip joint replacement
30. Knee meniscus injuries
31. Congenital diseases of children
32. Congenital dislocation of the hip joint
33. Children’s limp
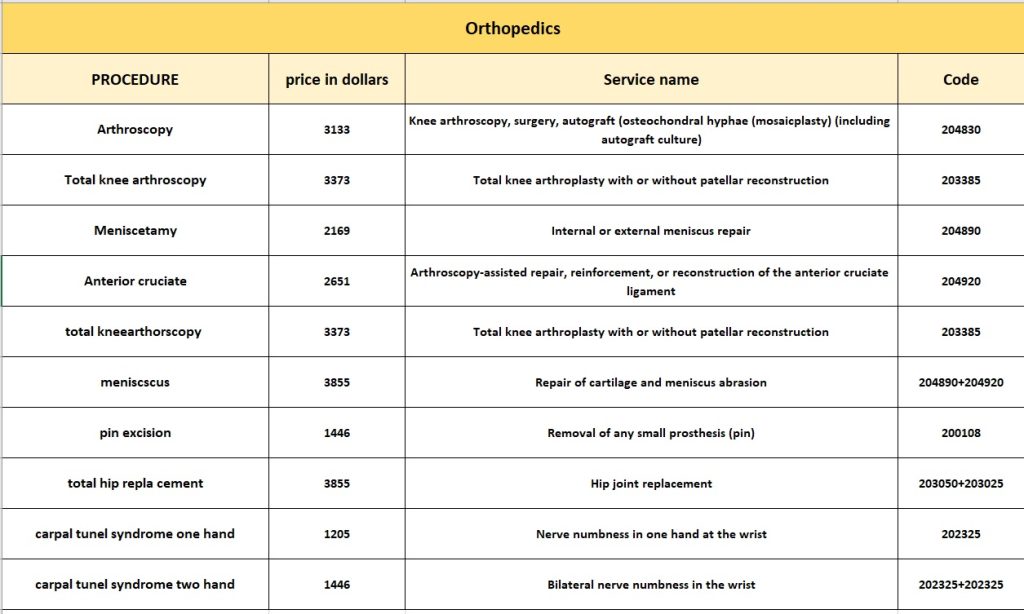
Surgical Orthopedic Treatments
The following sections discuss some of the surgical procedures that an orthopedist may perform as part of their practice.
Total Joint Replacement (TJR)
In this type of surgery, the worn-out and damaged joint is replaced, and a prosthesis is used as a replacement to restore joint function. Many people are able to return to their daily activities more quickly than before after a TJR.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that uses an arthroscope to diagnose joint problems. The arthroscope is a long, thin camera that an orthopedic surgeon inserts into a person’s joint, usually the knee or shoulder.
Fracture Repair Surgery
An orthopedic surgeon may recommend reconstructive surgery to restore the normal anatomy of a bone in the event of a severe fracture. They can use various types of implants, such as rods, plates, screws, and wires, to stabilize the bone. After surgery to repair a fracture, a person usually loses muscle strength and range of motion in the injured area.
Bone graft surgery
Orthopedic surgeons may use bone grafts to increase bone regeneration when a person’s body is unable to produce enough new bone.
Spinal fusion
In spinal fusion surgery, a doctor fuses two or more vertebrae together to correct a spinal problem. This procedure allows the vertebrae to fuse into a single mass of bone.
Non-surgical orthopedic treatments for injuries
• Joint injections, such as cortisone or steroid medications, or viscoelastic supplements.
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
• Physical therapy to reduce muscle spasms or improve muscle strength.
• Orthotics, custom-made shoes that support the proper position of the foot.
How to follow up on international patients:
1- Follow-up by an international patient expert:
The patient’s condition is monitored by the hospital’s international patient expert through social networks for 2 days and one week after discharge, and all patient status follow-up is recorded in the relevant office.
2- Follow-up By the relevant company:
The patient’s condition is monitored by the international patient company, and if necessary, the relevant company will contact the introduced international patient expert.
Prices are approximate and may vary depending on the patient’s condition.
Adress: Zakizade st – Seol st – Tehran – Iran Phone:+982141014 Email:info@armanhospital.com Expert International Patient(Mr.Shahab mirkazemi): +989366161448